Fabrication in Engineering: A Complete Guide
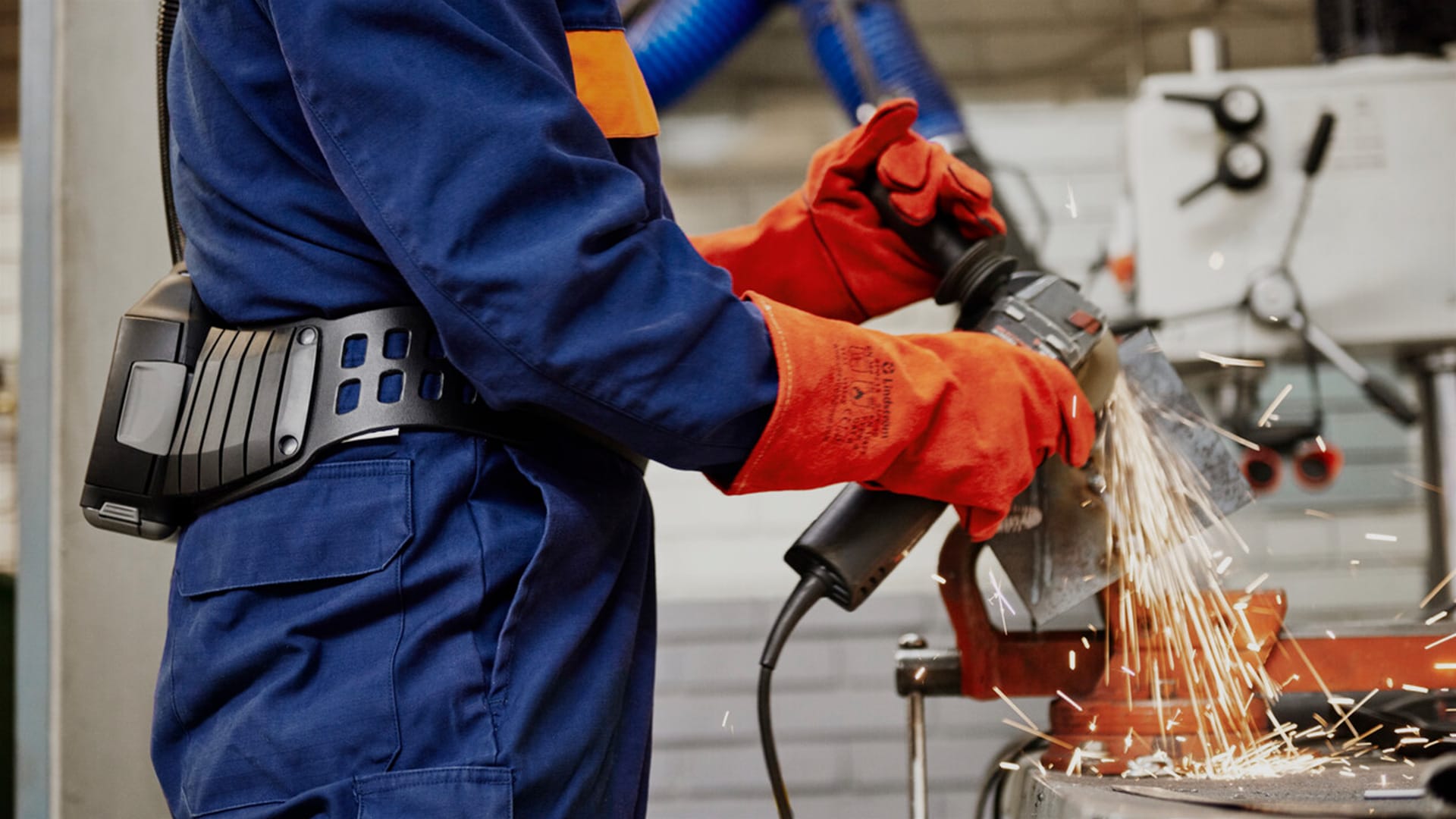
Fabrication plays a vital role in modern engineering. It involves shaping and assembling components that form the backbone of everything from industrial machinery to high-precision electronics.
While often linked with manufacturing, fabrication focuses specifically on creating individual parts, rather than entire finished products.
This guide explains what fabrication means in engineering, how it differs from manufacturing, and outlines real-world examples, essential processes, and industry applications.

What Is Fabrication in Engineering?
Fabrication refers to the process of creating parts, structures or assemblies through operations such as cutting, bending, and joining materials.
In engineering, this usually involves working with metals to produce components used in construction, equipment, or industrial systems.
The process is highly valued for its precision and adaptability, especially in industries that require customised parts or consistent replication of complex designs.
Real-World Example
In a car production facility:
- The fabrication team may create the metal framework for a car door using laser cutting and welding techniques.
- The manufacturing team oversees the full vehicle assembly, incorporating the fabricated parts alongside other systems.
This distinction highlights the focused nature of fabrication compared to the broader scope of manufacturing.

Key Fabrication Processes Used in Engineering
Fabrication involves a series of technical processes, each contributing to the creation of reliable and accurate components. The most common fabrication methods include:
Cutting
Engineers use tools such as laser cutters, plasma torches, waterjets or CNC-guided saws to trim raw materials to precise sizes.
Bending and Forming
Press brakes and rollers are used to bend sheet metal into exact shapes, making this step essential for frames, panels and brackets.
Welding and Assembly
Parts are joined through welding methods such as MIG, TIG or spot welding. These processes ensure strong, lasting joints suitable for high-stress environments.
Punching and Stamping
Punching presses are used to create holes or patterns in materials, often for functional or aesthetic purposes.
CNC Machining
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems automate cutting, drilling and milling using digital design files, which allows for consistent high-precision work.
What Is Metal Fabrication?
Metal fabrication is a specialism within fabrication that focuses on metals such as steel, aluminium and copper. It is widely used in sectors that demand strength, durability and corrosion resistance.
Common Applications of Metal Fabrication
- Steel beams and columns in construction
- Chassis and brackets in the automotive sector
- Mounting panels and cases in electronics
- Machine frames in manufacturing facilities
Fabricated metal components are often developed using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software and brought to life with CNC machines for maximum precision.

Fabrication vs Manufacturing: Understanding the Difference
Fabrication and manufacturing are closely related but serve different functions within the production process.
| Fabrication | Manufacturing |
| Focuses on producing individual components | Covers the full process from raw material to finished product |
| Involves techniques like cutting, bending and welding | Includes planning, fabrication, assembly, and packaging |
| Often used in mechanical, structural and custom builds | Applied to mass production across many industries |
While fabrication is often part of a manufacturing process, the two should not be confused. Fabrication focuses on component creation, whereas manufacturing includes the entire lifecycle of a product.
How CNC Machining Supports Fabrication
CNC machines allow engineers to create complex components with high accuracy. These machines follow programmed instructions, removing human error and increasing repeatability.
Key Benefits of CNC in Fabrication
- Precise shaping of materials using digital instructions
- Efficient mass production of customised components
- Improved safety and consistency across projects
Coolant systems play an important role in CNC operations. They reduce heat during cutting, protect the tools and prevent material deformation. Maintaining these systems is essential for optimal machine performance.
Keeping Fabrication Facilities Clean and Compliant
During fabrication, substances such as oil, coolant, and metal debris can create safety risks or cause machinery issues. Clean workspaces are not just a matter of hygiene; they help reduce downtime and improve productivity.
Lindström’s Industrial Wipers and Mat Services
Lindström provides engineering teams with engineering wipers and absorbent mats designed specifically for fabrication settings.
Industrial Wipers
- Reusable and highly absorbent
- Ideal for cleaning surfaces, tools and spills
- More sustainable than disposable rags
Absorbent Mats
- Placed beneath CNC and fabrication stations
- Prevent coolant and oil from spreading
- Help maintain a safer work environment
These services also support environmental compliance through regulated waste disposal and water recycling.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is fabrication in engineering?
Fabrication is the process of constructing parts or structures by cutting, shaping and assembling materials, typically metals, in engineering and industrial settings.
What is metal fabrication?
Metal fabrication involves the creation of metal components through cutting, bending and joining processes used across a range of industries.
Is fabrication the same as manufacturing?
No. Fabrication is a specific stage in the production process focused on part creation, while manufacturing includes the full transformation of raw materials into final products.
What is the difference between fabrication and manufacturing?
Fabrication is about making components. Manufacturing includes fabrication but also involves assembly, testing and finishing.
What tools are used in fabrication?
Fabrication relies on tools such as press brakes, welders, cutting machines and CNC systems to produce parts accurately and efficiently.
Final Thoughts
Fabrication is a specialised and essential aspect of engineering. From designing structural frames to producing finely machined components, the process plays a key role in building the elements that underpin modern industry.
For businesses managing fabrication equipment and facilities, maintaining cleanliness and efficiency is just as important as precision.
Lindström’s rental solutions for industrial wipers and absorbent mats help engineering teams stay productive, compliant and ready for every project.
Get in touch with Lindström UK to learn how we support fabrication professionals across the country. Lindstrom is an ISO 14001 accredited company, and our service is ISO 9001:2000 certified.